Dupixent (dupilumab) stands out as a fully human monoclonal antibody that has gained recognition for its therapeutic effects in multiple inflammatory conditions that involve the immune system. Dupixent received initial US FDA approval to treat atopic dermatitis along with asthma and chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis before expanding its investigation to chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU). This article provides a detailed examination of Dupixent's pharmacology, clinical efficacy, and application for treating hives, with a focus on chronic spontaneous urticaria.
What is Dupixent and how does it work?
Dupixent functions as a monoclonal antibody by binding to the interleukin-4 receptor alpha (IL-4Rα), which serves as a common element of the receptors for both interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-13 (IL-13). The cytokines IL-4 and IL-13 play fundamental roles in triggering inflammation and immune system reactions across multiple allergic disorders. Dupixent regulates allergic and inflammatory disease responses by disrupting the signaling pathways of Th2-cytokines.
Dupixent attaches to IL-4Rα, which blocks the JAK-STAT pathway activation and thus hinders IL-4 and IL-13 activity. The therapeutic action interferes with several inflammatory processes by disrupting skin barrier dysregulation alongside IgE class switching and Th2 differentiation, which are critical elements in diseases such as atopic dermatitis and asthma. Dupixent works by altering the immune response in CSU, which decreases histamine production and helps lessen itching and hives.
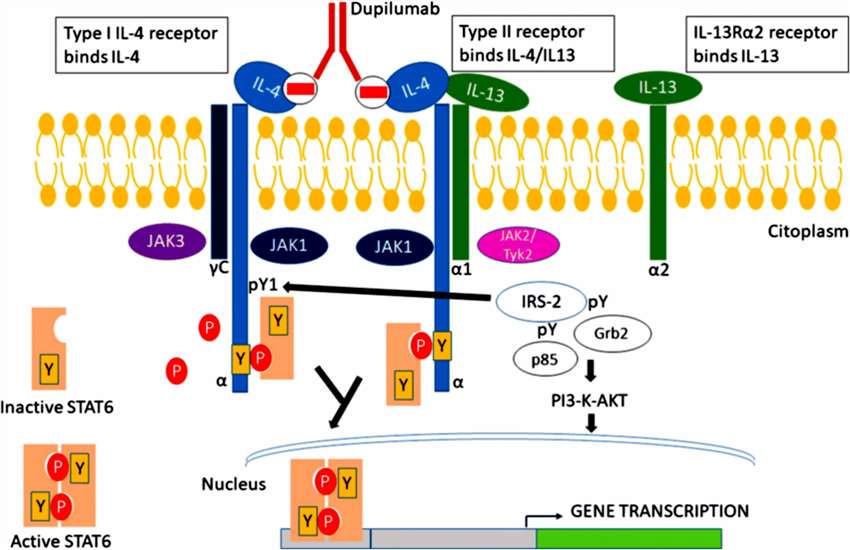 Figure 1. Mechanism of action of Dupilumab[1].
Figure 1. Mechanism of action of Dupilumab[1].
What are the key indications for Dupixent?
The medical community recognizes Dupixent as a versatile treatment option in immunology and dermatology because it has been approved to treat a broad range of conditions. After its initial approval for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis treatment, Dupixent obtained further approval for different conditions.
| CSU | Dupixent remains under study for its effectiveness against CSU, which shows symptoms of sudden hives and itching that occur without identifiable triggers. Patients who did not respond well to traditional antihistamines experienced notable reductions in urticaria symptoms and itch intensity after Dupixent treatment, according to clinical trial findings. |
| Asthma | Dupixent serves as an additional maintenance treatment for moderate-to-severe asthma patients who exhibit high levels of eosinophils. |
| Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis (CRSwNP) | Patients with this condition characterized by continuous sinus inflammation and nasal polyps can be treated with this approved medication. |
| Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) | Dupixent successfully reduces eosinophilic inflammation in the esophagus, which serves as a primary indicator of EoE. |
The FDA's review process for the CSU application is currently underway, with an anticipated decision date of April 2025.
How effective is Dupixent for chronic hives?
Current clinical studies have shown that Dupixent works well for treating chronic spontaneous urticaria. Dupixent showed significant improvement in reducing both the severity of hives and itching among CSU patients according to the LIBERTY-CUPID Phase III clinical trial series that included studies A, B, and C.
In Study C, researchers studied biologic-naive individuals whose chronic spontaneous urticaria remained uncontrolled despite standard antihistamine treatment. The trial achieved its main research goals by demonstrating a substantial decrease in both urticaria activity and itch severity.
The safety profile of Dupixent for CSU treatment matched its safety profile across other medical indications. The primary adverse events reported consisted of mild reactions at injection sites along with a higher occurrence of COVID-19 infections. Patients could manage these adverse effects without needing to stop their therapy.
Dupixent offers substantial therapeutic advancements over H1 antihistamines,, particularly for patients whose conditions remain uncontrolled with standard treatments. A complete strategy for managing CSU emerges when treatments address its root inflammatory mechanisms instead of only symptom relief.
 Figure 2. Phase 3 trial of dupilumab in chronic spontaneous urticaria (LIBERTY-CSU CUPID)[2].
Figure 2. Phase 3 trial of dupilumab in chronic spontaneous urticaria (LIBERTY-CSU CUPID)[2].
What are the pharmacokinetics of Dupixent?
A thorough understanding of Dupixent's pharmacokinetics forms the basis for developing its dosing schedule and assessing its treatment effectiveness. Patients who receive Dupixent through subcutaneous administration achieve steady-state drug concentrations after 16 weeks of consistent dosing.
After subcutaneous injection, Dupixent reaches peak plasma levels within one week because it is absorbed rapidly. The bioavailability of the drug Dupixent remains consistent between 61% and 64% among different patient groups who suffer from atopic dermatitis, asthma, and CSU.
The medication maintains a distribution volume of about 4.8 liters and undergoes primary elimination through catabolic degradation into smaller peptides and amino acids like other monoclonal antibodies. Plasma concentrations reduce to undetectable levels within 9–13 weeks for adults, while pediatric patients aged 6 months to 5 years experience a marginally extended elimination duration.
What kinds of side effects should patients expect when taking Dupixent?
Like other biological drugs, Dupixent presents a potential risk for side effects. The most commonly observed adverse events include:
- Injection Site Reactions: Patients often experience pain, redness, or swelling at the administration site; these symptoms resolve over time.
- Infections: Upper respiratory tract infections occur more frequently among patients, but COVID-19 infections can also develop in some cases.
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Although rare, severe allergic reactions can occur. Healthcare providers must continuously watch patients for symptoms indicating anaphylaxis.
The adverse events recorded during clinical trials appeared mild to moderate and matched the safety profile of the drug for its other indications.
How does Dupixent compare to other treatment options for hives?
Dupixent uses a unique treatment mechanism that sets it apart from conventional hives therapies, which mainly depend on antihistamines and corticosteroids. This table compares Dupixent with standard treatments for chronic spontaneous urticaria.
| Treatment | Mechanism of Action | Efficacy | Side Effects |
|---|
| Dupixent | IL-4Rα inhibition, targets Th2-mediated inflammation | Significant reduction in itch and hives | Injection site reactions, infections |
| H1 Antihistamines | Histamine receptor antagonism | Reduces histamine effects, but less effective in severe cases | Drowsiness, dry mouth, dizziness |
| Corticosteroids | Anti-inflammatory, suppress immune response | Effective for short-term flare-ups | Weight gain, increased infection risk |
| Omalizumab | Anti-IgE monoclonal antibody | Effective for CSU, especially in refractory cases | Headache, injection site reactions |
The focused treatment approach of Dupixent stems from its mechanism, which targets key cytokines involved in inflammation.

The extended use of Dupixent for chronic spontaneous urticaria provides patients with a new effective treatment choice for managing this challenging condition. The possibility of Dupixent becoming an approved treatment for hives represents a major step forward in managing this long-term condition while regulatory bodies assess its use in CSU. Alfa Chemistry remains focused on research developments to maintain Dupixent's effectiveness across multiple therapeutic fields.
Related Products & Services
References
- Lázaro-Sastre M., et al. Dupilumab in Atopic Dermatitis. Current Treatment Options in Allergy. 2019, 6, 210023.
- Maurer M., et al. Dupilumab in patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria (LIBERTY-CSU CUPID): Two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials. Anaphylaxis, drug allergy, urticaria, and angioedema. 2024, 15(1), 184-194.
Please kindly note that our services are for research use only.

 Figure 1. Mechanism of action of Dupilumab[1].
Figure 1. Mechanism of action of Dupilumab[1]. Figure 2. Phase 3 trial of dupilumab in chronic spontaneous urticaria (LIBERTY-CSU CUPID)[2].
Figure 2. Phase 3 trial of dupilumab in chronic spontaneous urticaria (LIBERTY-CSU CUPID)[2].
